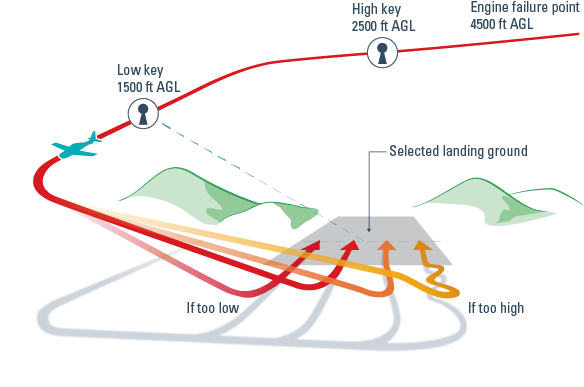
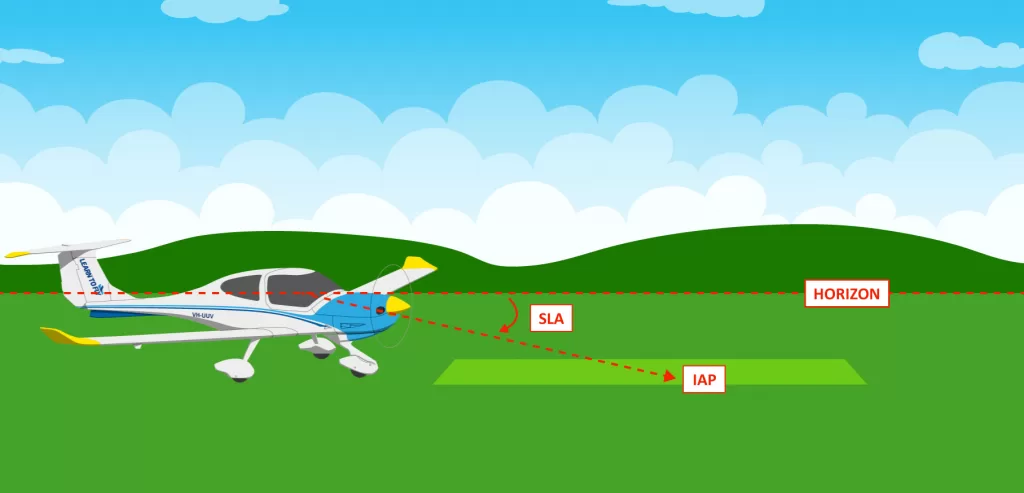
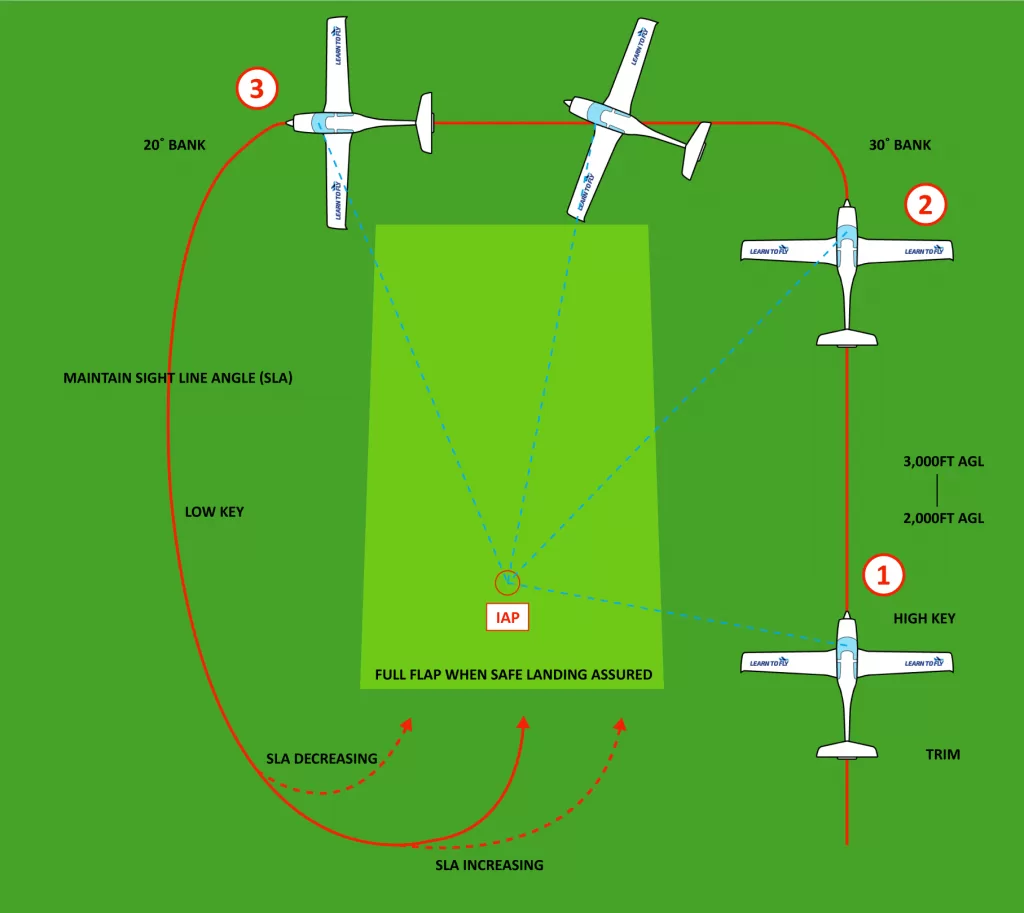
As technology progresses faster and faster in the modern world, there are many processes that are becoming automated. So where do human factors in aviation sit in an increasingly automated world?
What are human factors?
Even with automated tasks and processes, humans still need to either control, manage, intervene, or interact with technology at many stages.
Human Factors in its widest definition describes all the many aspects of human performance which interact with their environment to influence the outcome of events. These may be related to either the physiological or psychological aspects of human capability. Both of which are able to directly affect the way in which the human operator performs in different circumstances.
Human Factors knowledge reduces the likelihood of errors, and builds more error tolerant and more resilient systems.
What are the effects of human factors in aviation?
Things have changed a lot from when we had to manually start an aircraft’s propeller. And also from when pilots had to exclusively use landmarks to visually navigate during flight. But even with all of the latest technology installed in aircraft, human factors still play an enormous role.
The human factors involved in the operation and interpretation of even the most modern technology remain of the utmost importance in ensuring the safety of aircraft operations.
Negative human factor impacts
Most of the world’s worst aviation disasters have been a direct result of human factors, including the following. An example of this is the Tenerife disaster in 1977. A runway collision between two B747 airliners, due to misinterpreted radio communication form the captain of one of the aircraft. It resulted in 583 casualties.
There are examples of failed interactions between humans and technology. One such incident is the mid-air collision between a chartered Tu-154 passenger flight and a B757 DHL cargo jet over Überlingen, Germany in 2002. This resulted from ambiguous air traffic control and TCAS (traffic collision avoidance system) instructions. The automated TCAS instructions were in fact correct in warning the pilots of nearby traffic. It directed them to change their respective altitudes accordingly. The intervention of a fatigued air traffic controller however, who was unable to access the full scope of information he needed, resulted in the TCAS instructions being ignored, and the aircraft collided.
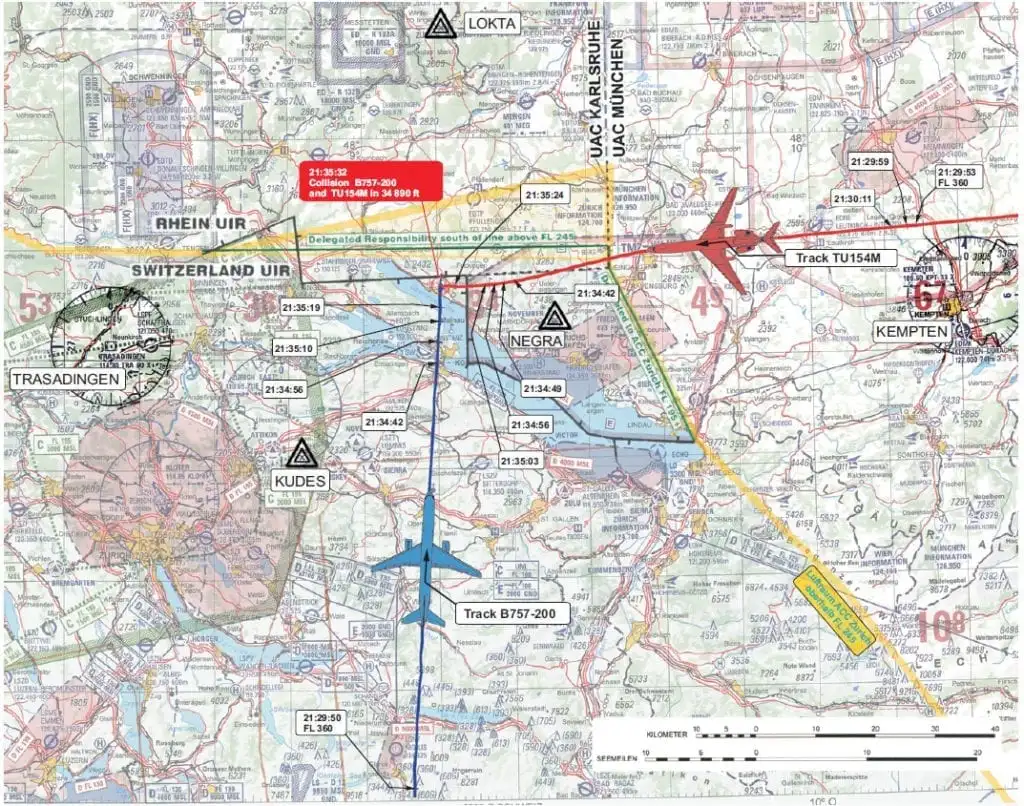
Positive human factor impacts
Whilst human factors such as stress, fatigue and psychology can no doubt be discussed in relation to negative impacts on aviation, there are many situations where human factors are essential to the safe operation of a flight.
Most technology still requires a human to either operate it, manage it or translate it. In flight in particular, there are so many variables that at this stage it is very difficult to rely entirely on an automated system to make decisions.
A perfect example of the above lies in the recent tragedies involving Boeing 737MAX aircraft. This led to the grounding of the aircraft globally while software systems were checked and upgraded. There is evidence to support that the failing system was overridden by a pilot on the LionAir aircraft during flight the day before the subsequent accident occurred.
Investigation into human factors decisions that have proven to be efficient in breaking a chain of events that would have led to an accident is very important in improving aviation safety overall. This is helping to develop better technology.
Would you trust flying in an entirely automated aircraft?
The only way to eliminate human factors in aviation contributing to accidents is to completely eliminate human involvement. In other words, become 100% automated. But is this feasible, and would you trust an entirely automated aircraft?
The use of commercial and military drones shows the technology for pilotless plane travel exists and is in regular use. But whilst the world’s most common types of passenger aircraft rely heavily on computers to execute the commands of pilots and crew, a completely unmanned flight poses many potential issues.
Would there be teams of pilots on the ground controlling the aircraft? Who is in charge of the plane when it is in the air, and what would happen if an emergency situation with a passenger on board occurred?
It is incredibly difficult to think of scenarios that would not require human involvement at some level. Therefore, human factors are still relevant at some point in the process.
What do pilots think?
Naturally, pilots are concerned about flight safety. Steve Landells, flight safety specialist for the British Airline Pilots Association, says:
“Automation in the cockpit is not a new thing – it already supports operations. However, every single day pilots have to intervene when the automatics don’t do what they’re supposed to. While moving pilots to a control tower on the ground might eventually save airlines money, there would need to be huge investment to make this possible, and even more to make it safe.”
Where do human factors fit in the future of aviation?
Negative human factor influences may be accountable for most aviation accidents. But how many accidents have been avoided through positive human factor intervention?
The study of human factors in relation to aviation is incredibly important to maintain and improve the safety of flight operations in today’s world, as well as for the future of air travel.
With technology accelerating and offering more in the way of automation, the nature of the relationship between human factors and aviation will continue to change. Human management, interaction and involvement with technology and automated processes in aviation now is no less crucial than it was in the management of fully manual processes in the past.
We have developed our own Human Factors Awareness Training course, that all of our staff attend. This course is also open external applicants who want to learn more about human factors in aviation. To learn more, chat to one of our flight training specialists. Email hello@learntofly.com.hk/en or go to https://drift.me/learntofly/meeting to book a meeting and school tour.